What is leaky gut syndrome? Learn more about this condition and how it impacts your gut health below
RELATED: Why Gut Health Matters More Than You Think
What Is Leaky Gut Syndrome and Other FAQs
What Is Leaky Gut Syndrome?
The term “leaky gut” describes the increased permeability of the intestines. The medical term is leaky gut syndrome.
How do the intestines become permeable? The intestines are responsible for different functions, including the absorption of nutrients.
They also distribute these vitamins, minerals, and enzymes to the bloodstream. This way, your cells can use them.
Here’s the thing, though. Millions of microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, live in the intestines.
Many of them are active. They produce chemicals that may be harmful to humans if they end up leaving the gut.
Meanwhile, the bloodstream carries a good amount of toxins that are by-products of the different organs. These can include the liver.
To make sure these toxins don’t enter the bloodstream or the gut, the intestines have a barrier or a wall called the tight junction. In here are small gaps that allow only those that should be in the bloodstream to pass through.
The problem is this wall can become weak or loose. When it happens, the bacteria, digested food, and toxins in the gut may find their way into the bloodstream while toxins get mixed up in the intestines.
It is believed this can trigger the increased risk of inflammation and even autoimmune disease, among other health conditions.
What Are the Symptoms of a Leaky Gut?
The following are some of the most common leaky gut symptoms:
- Changes in bowel movement (e.g., chronic constipation or diarrhea)
- Bloating and gas
- Poor immunity
- Lethargy and fatigue
- Nutritional deficiency
- Memory loss or brain fog
- Changes in mood
- Skin problems, such as acne and psoriasis
- Food sensitivity, allergy, or intolerance
- Joint pain
What Causes Leaky Gut?
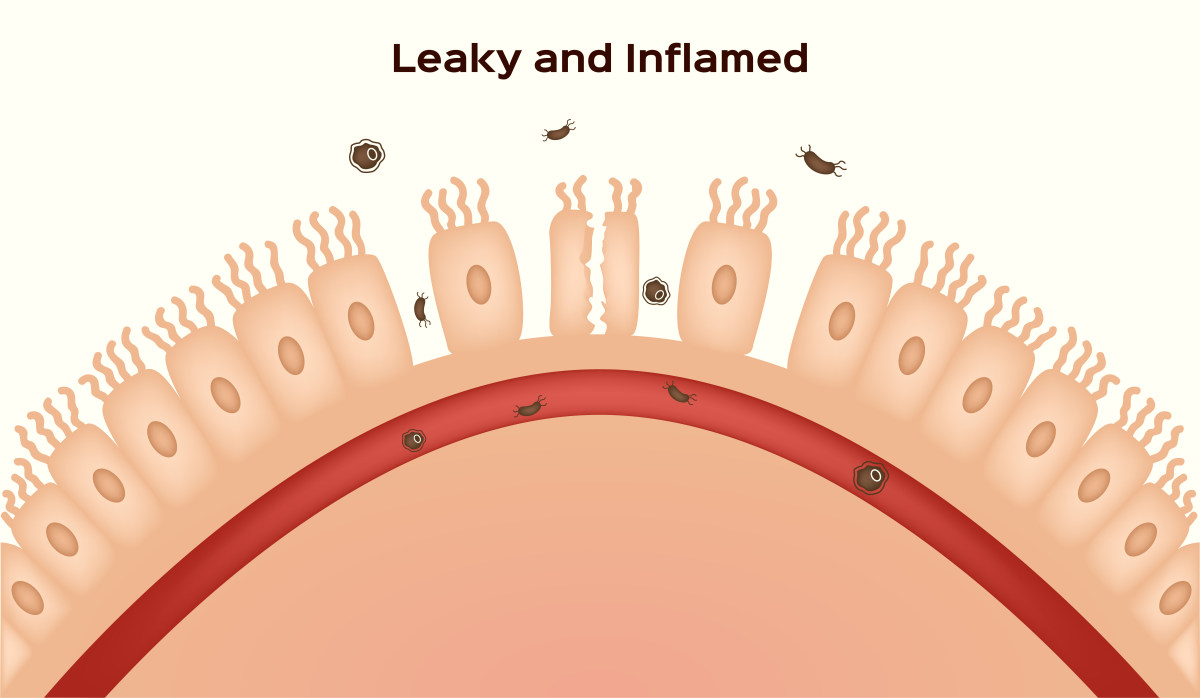
We can also answer the question “What is leaky gut syndrome?” by understanding how it occurs in the first place.
The actual cause of the leaky gut syndrome remains unknown, but there are risk factors. One of these is celiac disease.
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition characterized by the inflammation of the intestines due to a severe reaction to gluten, a type of protein mixture present in several kinds of wheat.
A 2006 study in Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology revealed that it may activate zonulin, the protein that regulates the permeability of the intestines or their tight junctions.
The researchers found the same result in people with the non-celiac disease, although the increased permeability was more severe among those with the condition.
Another risk factor is stress, especially in connection to the gut-brain axis. This axis means that the intestines and the brain are co-dependent via the vagus nerve.
When a person is under stress, the body releases a chemical known as corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF). It stimulates the creation of other chemicals that regulate stress hormones such as cortisol.
The brain produces CRF, but so does the gut, which means its release can directly impact the digestive system. One of the possible changes is increased permeability.
RELATED: 4 Steps To Heal Leaky Gut And Autoimmune Disease
Is a Leaky Gut an Autoimmune Disease?
A leaky gut is not an autoimmune disease, which is a condition wherein the body’s own immune function goes haywire and begins attacking itself. It happens because the immune system may recognize what can be a harmless substance as a foreign invader.
Problems in the gut, however, including leaky gut syndrome may encourage or worsen autoimmune diseases. These can include type 1 diabetes, celiac disease, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Many studies established a link between a leaky gut and some of the common chronic and autoimmune diseases. A good example is type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition characterized by the destruction of cells in the pancreas, which produces insulin. A study over 15 years ago reported that those with type 1 diabetes also had an increased intestinal permeability.
It’s the same pattern determined among individuals predisposed to Crohn’s disease. A leaky gut is common among this population, and it occurs even before the actual symptoms of the disease appear.
Leaky gut may also develop through exposure to substances that can likely change the gut flora:
- Medications such as antibiotics
- Chemicals, preservatives, and additives found in processed foods
- Alcohol
How Do You Test for a Leaky Gut?
To restore your gut health, it’s essential to know how it works so you may have to consider taking a leaky gut test.
The problem is this issue doesn’t have a single official exam. Some doctors may recommend a food intolerance test or a food allergy test.
Two of the most popular options are the zonulin test and the lactulose-mannitol test, which are helpful in screening people for celiac disease.
In the zonulin test, the doctor looks for elevated levels of the protein. It can increase due to a reaction to gluten and the presence of certain types of bacteria.
What Foods Should You Avoid If You Have Leaky Gut Syndrome?
You may start healing your leaky gut if you avoid the following:
- Foods with gluten such as bread (this is a must for people with celiac disease)
- Those with sugar and dairy as they may change the balance in the gut flora
- Processed foods, especially ultra-processed ones
- Sweetened beverages and alcohol
- Refined oils
- Junk food and fast food
- Pre-made baked goods since they tend to contain high amounts of carbs and sugar
What are ultra-processed foods? These are the types of food that underwent several manufacturing processes to extend their shelf life, texture, and flavor.
Instead, you can learn to heal a leaky gut by doing the following:
- Eating more fruits and vegetables, including potent green blends
- Increasing the intake of fiber-rich foods as bacteria feed on them (the more you consume them, the more the intestinal barrier strengthens)
- Taking antibiotics as prescribed by the doctor
- Reducing your stress levels
- Consuming foods rich in probiotics such as sauerkraut
Is Leaky Gut Real?

There’s a much bigger question than “What is leaky gut syndrome?” This is whether it exists or not.
Despite the growing popularity of leaky gut syndrome, it is still not an official medical diagnosis. The scientific community still does not agree on many issues about it, especially if it exists in the first place.
The Canadian Society of Intestinal Research said there’s not enough evidence to corroborate the claim that it can cause conditions outside the digestive tract.
The bottom line is it requires a more intensive study just like other rapidly growing conditions in the world. The good news is the scientific community is learning more about it.
Hopefully, this post enlightens you to be able to figure out the symptoms of a leaky gut. Consider this as a wake-up call to pay more attention to your gut health.
The sooner you take care of it, the faster you can avoid more serious health conditions in the future.
You May Also Like…




